Fertility is the natural ability to reproduce an offspring both in human and animal, and arguably same in plants. Generally speaking, humans can either be male or female. Each sex possesses their varied and similar biological traits. Among the various human features such as irritability, nutrition, adaptation, respiration, etc., reproduction is the only feature that empowers us to recreate another or better versions of ourselves. As biological creatures we are to reproduce offspring for the continuity of life.
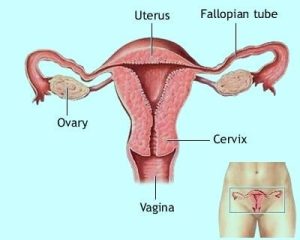
Female Reproductive System
While both the male and the female participate in the reproductive process, the bunch of it resides in the female. This is because from the point of conception to delivery, the new life (foetus) is in her body and if any part of her reproductive and body organs fails, the new anticipated life may fail too. What is more, the status of the female’s body determines whether conception will take place or not, to start with.
Fertility Versus Fecundity
Fertility in women begins early; barely 10 years after a girl is born. It has a beginning point (puberty) and an ending post (menopause). The female child is, under normal circumstances, born with all the accessories needed for childbirth. As the female matures or ages, so do her reproductive organs mature and age accordingly.
The reproductive organs of a female are awakened in puberty phase with the first menstruation (menarche) indicating readiness to conceive but not to birth a baby. This is because the other organs such as the fallopian tubes, cervix, uterus, etc. are not fully developed yet to form, nurture and convey the foetus out of the womb. Thus, though the female is fertile, she may not be able to conceive. This is what differentiates fertility from fecundity. Fecundity details the numerous factors that determine whether a fertile (ability to reproduce) female will reproduce or not. In essence, the female, despite being fertile, may restrict herself or may be restricted by biological conditions from giving birth to a baby. So many other reasons such as age (early or late), economic hardship, environment, genetic, career goals, personal choice and others can make the female not to reproduce. That is to say that fertility is biological while fecundity is about the disposition or readiness to harness and maximize ones fertility for reproduction.
Fertility Period And Pregnancy
The female body, as we already pointed out, has a period of fertility. It is gainful for women who wish to become mothers to embrace their most fertile years for child bearing. Such years come with less complications or problems arising from conceiving, gestating (bear the child in the womb) and delivering. Biologically, a woman’s fertility declines as she gets older. A female of 18 years is more fertile than a 25-year old woman. Age is therefore a primary factor for fertile women who feel they are not ready to become mothers. Being fertile encompasses a lot of considerations. It is beyond the monthly release of eggs (ovulation) from the ovaries. It extends to the functionality of the female’s reproductive organs. A failure or inadequacy of one organ while the other is efficient would not lead to success in making the woman a mother. For instance, a woman who’s uterus is efficient to nurture a foetus but her fallopian tubes are ruptured with cycst or her ova (eggs) are deteriorated may not successfully birth a baby. Likewise, a woman whose eggs or fallopian tubes are in good conditions but there is an absence of a uterus or the uterus is weak.
A woman can only be pregnant when all necessary conditions are met. This means that she has to ovulate; the ovulated egg must travel through the fallopian tube toward the uterus; sperms must swim up to the egg for fertilization and lastly, the fertilized egg must implant itself into the uterus (womb). Any alteration in these four prerequisites makes pregnancy impossible. Female’s infertility issues are woven around these four requirements needed for pregnancy to take place. Do not subtract the fact that her reproductive organs must be capable to sustain the foetus till delivery.
Causes Of Infertility In Women
When any of the female reproductive organs is deteriorated or damaged, preventing the woman from being pregnant or staying pregnant, the woman can be termed infertile. Infertility is the inability to conceive or nurture a zygote throughout the 40 (more or less) developmental weeks till delivery. A woman’s infertility can be caused by one or more factors. She is termed infertile when she is unable to get pregnant after six months or a year of engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse with the aim of conceiving. Women who are diagnosed infertile should not consider themselves barren without trying to fix the problem. Many infertility issues are curable and many women who had been infertile have successfully conceived after treatment. The only time when infertility becomes permanent (barrenness) is when it results from menopause, hysterectomy (removal of the womb) and other forms of removal of reproductive organs. These infertility cases are irreversible. Other infertile situations can be treated. The following are some of the known causes of infertility in women:
-
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):PID is an infection affecting the female’s reproductive organs such as the fallopian tubes, ovaries, cervix and the uterus. These organs are located at the pelvic region. When untreated or severe, it can scar and damage the fallopian tubes and the uterus. The bacteria responsible for PID are also those responsible for gonorrhea and chlamydia (STDs – Sexually Transmitted Diseases). PID can be caused by douching (which is un-recommended), having multiple sex partners, use of intra uterine devices for safety against unplanned pregnancy, unprotected sex, etc. It can also be hereditary. Patients of PID usually experience pain in the lower or upper abdomen, foul vaginal discharge, painful sex and urination. The bright news is that PID can be treated when still mild or at average but when severe, a surgery is usually needed.
-
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (POS): This infertility issue is triggered by excessive hormones. It can cause early, late or no period at all, leading to irregularities in the menstrual cycle. POS affects the ovaries and ovulation cycle of women between the ages of 15 and 44 years old. In this situation, the woman produces more than the needed hormones to regulate her cycle. It leads to cycst in the ovaries, high levels of male (androgen) hormones and irregular cycle. Effects of POS on women are severe Acne, depression, obesity, hair growth, irregular period, risk to cancer and high blood pressure. Unfortunately, POS can’t be cured but can be managed to help the female conceive and deliver children with strict medical supervision. Women with POS may be forced to limit the number of children they desire; usually, one or two kids may be the best choice. Management of POS requires a healthy diet to help shed off weight (most POS females are obese), hygienic measures to treat Acne and make hair growth mild. Birth control pills and diabetic drugs may be used while managing POS.
-
Endometriosis: This infertility issue is similar to POS but it is considered more harmful and tedious to control. A patient suffering from endometriosis often feels pain similar to POS such as pains in the pelvic, heavy mensuration, cramps, painful sex and other signs. Endometriosis simply suggests that the tissue that normally lines inside the uterus begins to sprout outside the uterus. The inside of the uterus is the endometrium. So the abnormality of the tissues growing outside the endometrium is tagged endometriosis. Females vulnerable to endometriosis are those with early cycle not up to 27days, kicked off menarche at a young age, have female relatives living with or have experienced endometriosis and lifestyles such as alcoholism and smoking. Just as POS, endometriosis can be mild or severe. Its complications make women infertile and have troubles with conceiving and staying pregnant. Ovarian cancer is another disease triggered by endometriosis.
-
Untreated Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs): STDs are not harmful if detected early and treated. Almost every female would contract one STD or more in their life time. Ironically, some STDs are not only communicable via sex. They can be contracted through exposure to bacteria looming mostly in the toilet or other human waste discharge environment. STDs are common cause of infertility disorders that may just play a small trick on women trying to conceive but snap out once treated with appropriate medication. Unlike other infertility disorders mentioned above, women with STDs, except for gonorrhea and chlamydia, may still conceive while having the infection. Pregnant women can still have traces of STDs without being aware. Other STDs are Human papillomavirus (HPV), syphilis, herpes, staphylococcus, etc. Their symptoms are mostly not conspicuous. This is why it is advised that active sexual females always engage in repeated medical checkups for tracking of STDs. They become salient via symptoms such as foul vaginal discharge, itching, spotting, changes in urination, sores, painful sex, etc. STDs can also be mild or severe. In severe cases, it can be a chasm for women trying to have a baby. STDs are the most easily managed fertility threatening cases. Just as the name suggests, STDs are mostly contracted through unprotected sexual involvement with an infected partner or keeping several sexual partners who also have infection. Other means of getting the infection, as stated above, are secondary.
-
Lifestyle Influence: Environment or lifestyle can also be responsible for preventing from being pregnant. A woman who is on constant birth control pills would have troubles when she finally decides to get pregnant. She may dedicate six months or a year trying to get pregnant. This is because the pills may have adversely altered her natural cycle, and therefore rendered her temporarily infertile. Lifestyle including stress, sedentary living, obesity, athletic training, poor diet, alcoholism, smoking, taking hard drugs (marijuana, nicotine), etc. threaten a female’s fertility. Also women who have one or more natural miscarriages or induced miscarriages (medical abortions) or late abortions may be rendered infertile, when not done professionally. Natural miscarriages also increase the risk for infertility. Medical abortions are safer for women than late abortions. Medical abortions have low possibility of affecting a woman’s fertility adversely if performed safely with clinical care. Women who are unhygienic especially with their underwear may be creating a paradise for bacteria which can render them infertile.
-
Fibroids: Fibroids are abnormal growth in or outside the walls of the uterus. Shockingly, every woman would have fibroids in their lifetime but the crux of the matter is the type of fibroid that each woman has. Fibroids block the fallopian tubes, change the shape of the uterus and weaken the lining of the uterus. There are various types of fibroids namely intramural, subserosal, pedunculated and submucosal fibroids. Intramural fibroids grow inside the muscular area of the uterus while submucosal grow in the middle muscle layer (myometrium) of the uterus. These two types of fibroids are the most disastrous and common. When severe, they render a woman permanently incapable of conceiving. Pedunculated fibroid develops into a stem shape around the uterus while the subserosal fibroid grows outside the wall of the uterus. Women between 30 to 40 years are at risk of having fibroids. At this age, the effects or signs of fibroids become pronounced. Largely, today’s women suffer from fibroids than in the past. This is because of changes in societies. Presently, most women begin to bear children from 30 years unlike before modernization and civilization. Previously, women began to bear children in their early 20’s and quit before or at 30 years old. Fibroids are caused by hormones (estrogen and progesterone), family history and pregnancy. Symptoms of this disease include swelling of the abdomen, increased urination, heavy bleeding and blood clots during menstruation, pelvic pain and so many others. Recommended drugs, massages, acupuncture and surgery (myomectomy) are various ways fibroids can be treated.
-
Age And Menopause: These are factors that are not ‘woman-made’. As humans, women must grow old and old age comes with its blessings and curses. Age and menopause are both natural ways that decline a woman’s fertility and make her infertile. As a female grows older, the quality of her eggs depreciates and the eggs reduce in number too. Age is the number one and unconscious factor that makes women become infertile. A woman’s fertile scale decreases rapidly after the age of 35. Women above this age would have more difficulty in conceiving due to decline in fertility than younger women. Women are advised to birth their children during their younger years in order to avoid complications that come with pregnancy in older women. Likewise, another natural infertility cause is menopause. This is the phase of a woman’s time when she no longer ovulates leading to a halt in menstruation permanently. Menopause is the absence of menstrual periods for a period of 12 months or more.
There is a myth that says that women who started menstruating at a younger age are liable to experience menopause early. Luckily, this is not a fact. The age a woman experiences menopause has no link with the age she has her menarche (first menstruation). Menstruation happens to women in different age brackets depending on various factors. These factors are dependent on the state of the woman’s reproductive system, hereditary issues, lifestyle, etc. For instance, women who smoke and have never been pregnant in their life are liable to experience menopause earlier than mothers and those who abstain from smoking and excessive consumption of caffeine. The age bracket for menopause is between 35 and 66 years. Menopause is a gradual process showing subtle signs as the woman advances in age. Hot flush or flashes, profuse sweating, stress, fatigue, mood swings, abnormal vaginal bleeding, itching, dryness, depression, etc. are some of the indications of menopause. These signs are to be controlled by the woman through socializing, constant medical checkups, quality dieting, spending time with loved ones, etc. The age and menopause factors cannot be eliminated but only managed.
Tips On Conception
Notwithstanding any type of infertility case a woman may encounter, once treated properly, her chances of conceiving and being delivered of a baby can be guaranteed. Of course, this applies to all infertility cases except menopause or hysterectomy which is irreversible. A fertile woman who desires to be pregnant should prioritize having sex during ovulation. This is the period when a woman produces a lot of eggs waiting for a sperm to fertilize them. Sexual intercourse during this period is likely going to result in pregnancy. The period can be ‘pre-ovulation’ (before ovulation), ‘on ovulation’ (during ovulation) and ‘post-ovulation’ (maximum of two days after ovulation). This is because these phases have the best luck to hit the jackpot. The ovum (egg) is ripe for fertilization; it’s anxiously waiting for an active, swimmable and efficient sperm.
Women who do not know when they are ovulating should track the days of their monthly cycle (the day a flow starts to the day another starts) and divide it by 2. For illustration, a woman with 30 days cycle would have her ovulation on the 15th day. It is calculated by counting from the first day of a woman’s period till the first day of the next menstruation. The number of days counted reveals the days of her cycle. To ascertain the ovulation day, the counted cycle days is divided by 2. It wouldn’t hurt to repeat the counting for a couple of months to be sure the woman has a steady days of cycle. The ovulation day is the peak, climax or height of a woman’s fertility. The good news is that research and experience has proven that most women long for sexual intimacy during this time as the urge is higher then. Women who are ready for childbirth should be sexually proactive closely before, during and just after ovulation.
Sperms can last from 5 to 7 days before dying. This means that the sperm can be in the woman’s body waiting for the released egg (between 5 to 7 days before ovulation), or just meeting the egg on spot (ovulation day) and perhaps meeting an awaiting egg (maximum of 2 days after ovulation). Do not forget to quit any contraceptive pill or practices when trying to become pregnant. Some women may need extra supplements to aid their goal. Always consult a physician before picking any supplements, natural therapies or drugs.
Apart from timing yourself, you also need to maintain a healthy living. Eat good food, desist from stressful activities (this is not to say that you should not exercise) and be mentally relaxed. One importance of eating healthy food when working towards pregnancy is to have a body disposed to form and nurture a foetus. In some cases, women become anemic when they conceive for shortage of red blood cells. The foetus is formed with blood, so one needs to eat good food, especially fruits and vegetables to ensure good health for the foetus and the mother.
In addition, some medically recommended drugs also prepare the woman’s body for child bearing. Most of these drugs contain folic/pteroylglutamic acid. This is some kind of supplement for vitamin, also used in the treatment of the nutritional anaemia mentioned earlier.
While we do not demean supernatural powers in childbirth, the roles of human being in making it happen should not be overlooked. Because there are biological and physical factors involved, one should try to take care of those. A healthy living attracts life; children are lives.
Guest Writer







